Scarlatine: signs on the tongue, buttons, contagion
La scarlatine est une maladie infectieuse causée par un streptocoque qui entraîne une angine, des boutons, une langue rouge... Est-ce grave ? Comment éviter la contagion ? Quels sont les traitements ? Quels risques chez la femme enceinte ? L'éviction scolaire est-elle recommandée ?
Definition
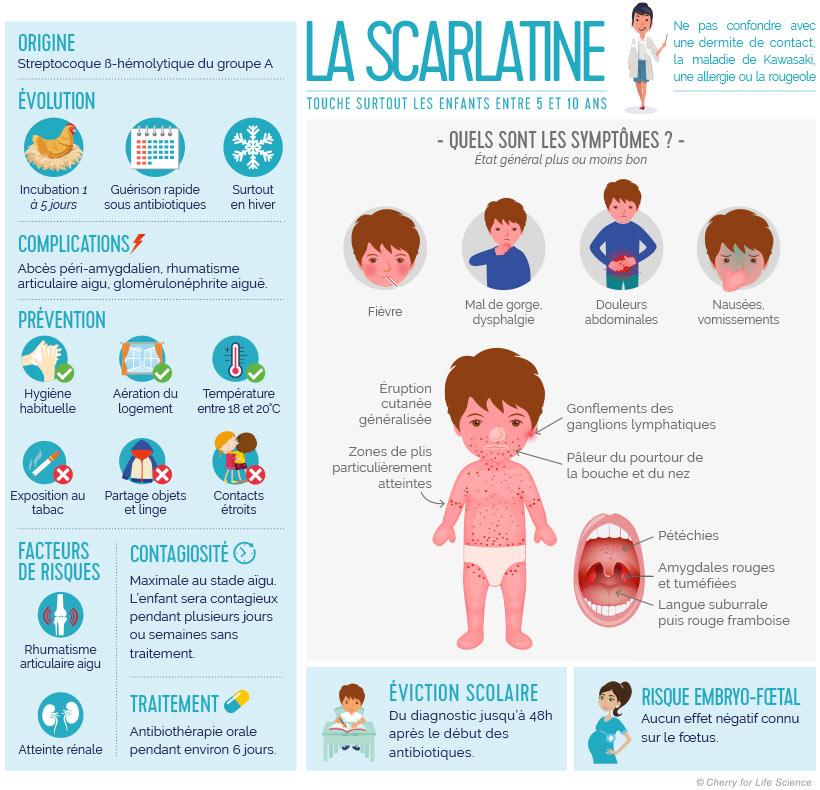
Scarlatin is a contagious infantile disease which most often affects children aged between 5 and 10 years during the winter, in small epidemics.They are caused by a bacteria called "group A streptococcus" and which is transmitted by inhalation of saliva droplets during sneezing, cough, kisses and indirect contacts (toys...)).
Incubation time
Streptococcus will enter the body and develop there until the symptoms appear.This latency period lasts on average between 3 and 5 days: it is the incubation time for scarlet.In adults, scarlatin is an exceptional disease.
Symptoms
Scarlatin manifests itself after the incubation period by a strong fever of sudden appearance, with angina, and cervical nodes. Quelques heures après apparaît une éruption cutanée donnant à la peau un aspect granité ou légèrement granuleux, d'abord sur le tronc, les plis de flexion (genoux, coudes)) puis les membres (sans atteinte de la paume des mains et de la plante des pieds)).It gradually extends to reach the cheeks and the perimeter of the mouth.This eruption is made in the form of large red plates and can be associated with itching.It is maximum after 2 or 3 days and disappears in about 6 days.A design then appears between the end of the first week and the end of the second week.She can last 3 weeks.Scarlatin can also cause abdominal pain, sometimes vomiting.The damage of the tongue is characteristic: of white, it becomes red (raspberry tongue typical of scarlatin)).
How to differentiate it from measles?
"Measles is characterized by an attack on the entire bronchopulmonary sphere, with conjunctivitis and an associated eruption.There is not an angina in the foreground as in the case of scarlatin "explains Dr Del Giudice, dermatologist specializing in infectious and tropical diseases and member of the French Society of Dermatology (SFD)).
3 Separate Family Members have smells this chain letter from the pope 🙃 https: // t.CO/5FXEMDE8SN
— Jen St. Jude ☄️ Sun Apr 05 23:36:34 +0000 2020
And with a handmain-blot?
"The symptoms of scarlatin are very different from those of the Pied-Main-Bouche syndrome which is characterized by small blisters in the mouth, feet and hands, without angina and without rash" informs the specialist.
Contagion
Scarlatin is contagious one day after the appearance of the first manifestations of angina and 24-48 hours after the start of the taking of antibiotics. Elle reste contagieuse jusqu'à la disparition des squames (3 semaines)) si un traitement antibiotique n'a pas été mis en place.The most frequent mode of contamination is made by direct contact with a healthy patient or carrier of streptococcus A, via pro-pharyngeal secretions.
Causes
Scarlatin is due to group A streptococcus.This streptococcus is responsible for a large number of benign infections such as erythematous angina, pharyngitis, impetigo.It can also cause invasive infections, such as toxic shock syndrome.Not treated with antibiotics, scarlet can cause complications, such as rheumatism with networks or renal or cardiac complications.These complications have become extremely rare in France.
Diagnostic
The diagnosis of scarlatin is clinical (it is made according to the signs observed)). Il est confirmé par un test de diagnostic rapide (TDR)) qui permet de mettre en évidence le Streptocoque.This test, also used for angina, consists of a sample that is done at the level of the throat.If the test is positive, antibiotics are prescribed.
Precautions, school eviction
Children being contagious until 48 hours after the start of antibiotics, they should not go to school for at least this duration.School eviction generally recommended by doctors is one week.There is not yet a vaccine against streptococcus a.The best prevention is to keep up to contaminated people.
Scarlatin and pregnancy;"We do not know a serious form in pregnant women" indicates Dr Del Giudice.
Treatment
Antibiotic treatment should be prescribed quickly to avoid kidney or heart complications. La scarlatine est traitée avec des antibiotiques comme Amoxicilline (en première intention)) pendant 5 à 6 jours.From the first 48 hours of administration, fever and symptoms of angina decrease. Un sirop antihistaminique (type Méquitazine)) peut être administré pour calmer les démangeaisons.Paracetamol can be prescribed in case of fever.
Thank you to Dr Pascal Del Giudice, dermatologist and member of the French Society of Dermatology.
Summary Definition Allpoints themptômesdifferent with measles Difference with the Pied-Main-BoucheConstagioncurs Diagnosis Precautions, Éviction Schoolgrossesstraitations Definition Definition...
I manage my push subscriptions
How to apply blush to change your face
GO
6 make-up brands available exclusively in Belgium
GO
Allylikes Spring Wear Complementary Ideas to look Fashion
GO
Bic pen, Duralex glass, Laguiole knife... thirty dream objects, designed and manufactured in France
GO